With a population of 10 million inhabitants, the provincial capital is a modern city, situated at the crossroads of Central China. In 2012, Wuhan’s GDP reached €94 Billion (an increase of 11.4% nominal GDP), being the 4th largest economy among sub-provincial cities[1]. Wuhan is a commercial centre of finance, industry, trade and science, with many international companies. Having scientific, technological and educational institutions such as Laser City and the Wuhan University, the city is also an innovation centre. Wuhan is a transportation hub for air, railway as well as ferry traffic. The distance from Beijing, Shanghai and Guangzhou is more or less equal. The Yangtze River and the Han River pass through the city. Wuhan has 13 districts and three state-level development zones, i.e. Wuhan Economic and Technological Development Zone (Zhuankou Development Zone), East Lake Hi-Tech Development Zone (Optical Valley of China) and Wuhan Wujiashan Economic and Technological Development Zone.
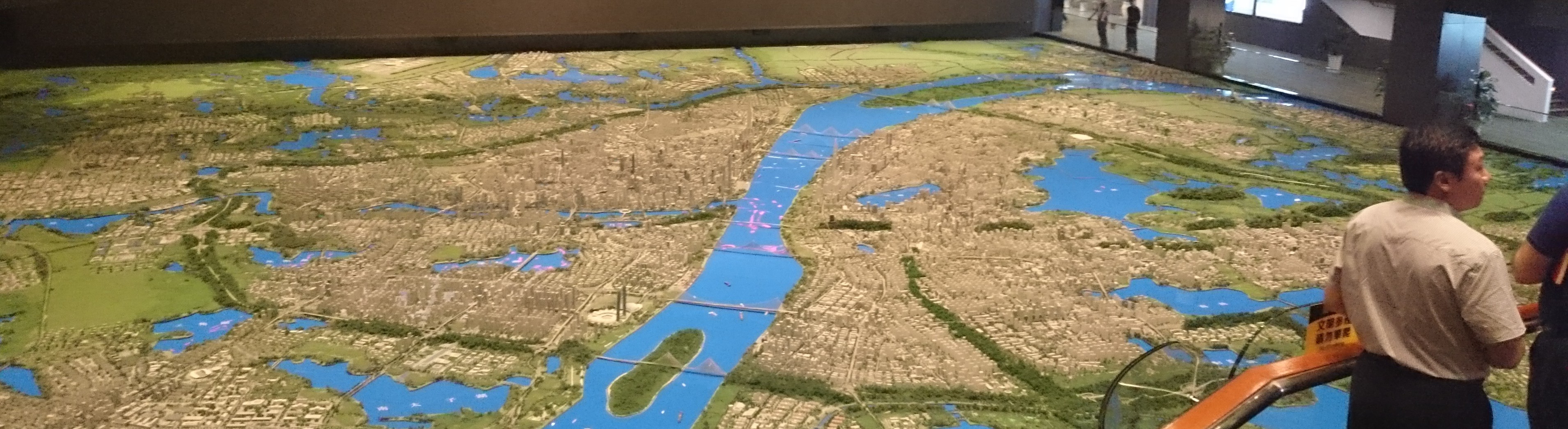
The polycentric urban pattern is confirmed in the Wuhan Masterplan. It describes the outlines of a green and blue framework in which the urban nodes are located and separated. The green area in the outskirts penetrate into the core zone of city’s urban network, mitigating the effect of ‘heat-islands’, establishing ecological corridors and separating the urban nodes. Six open wedges between the urban nodes are designated. They represent inherent values of ecology, landscape, agriculture, water storage. To ensure protection of these open spaces and green-blue wedges, the Masterplan has identified zones forbidden or restricted for use as urban construction land.
In August 2013, NDRC ratified Wuhan’s Low-carbon Urban Development Plan. By 2015, the city’s green areas should account for 28% of the city. Also 2.000 new hybrid buses will appear on local roads and 20% of all new buildings will be eco-friendly[2]. The plan also includes several activities in the logistics area.
Wuhan is demo zone for Cooperation Framework on “Sustainable Urban Development” between China and France. The city has also been involved in the CETREGIO programme since 2010.